What if our planet today was a giant Earth twice its current size and 10 times more massive? Everything will be incredibly different. And it is not thanks to the rings that the infant Sun had that prevented the Earth from developing in this direction.
according to NASA, 30% of the Sun-like stars in our galaxy orbit the super-Earth.
The sun of children will have rings like Saturn
Technology combined with optimizing data collected in the universe allows creating scenarios of what the Earth and the Sun would be like in their Earthly states. As such, the occurrence of super-Earths in many other solar systems has left astrophysicists with some unanswered questions, Rice University astrophysicist Andre Isidoro in Houston notes.
To know the investigator team Create a simulation model By computer to form the solar system, which emerged from the ashes when a cloud collapsed between dust and gas, known as the solar nebula.
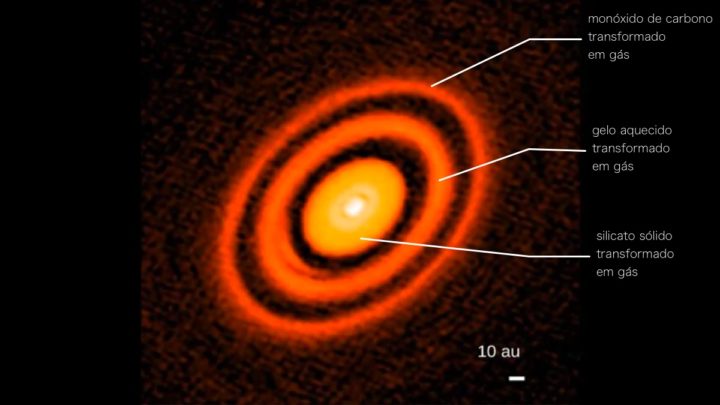
Their simulations suggested that pressure "collisions," or high pressure regions of gas and dust, would have surrounded the young sun. It is likely that these areas of high pressure are the result of the movement of molecules towards the Sun under the influence of its strong gravity, heating, and the release of large amounts of vaporized gas.
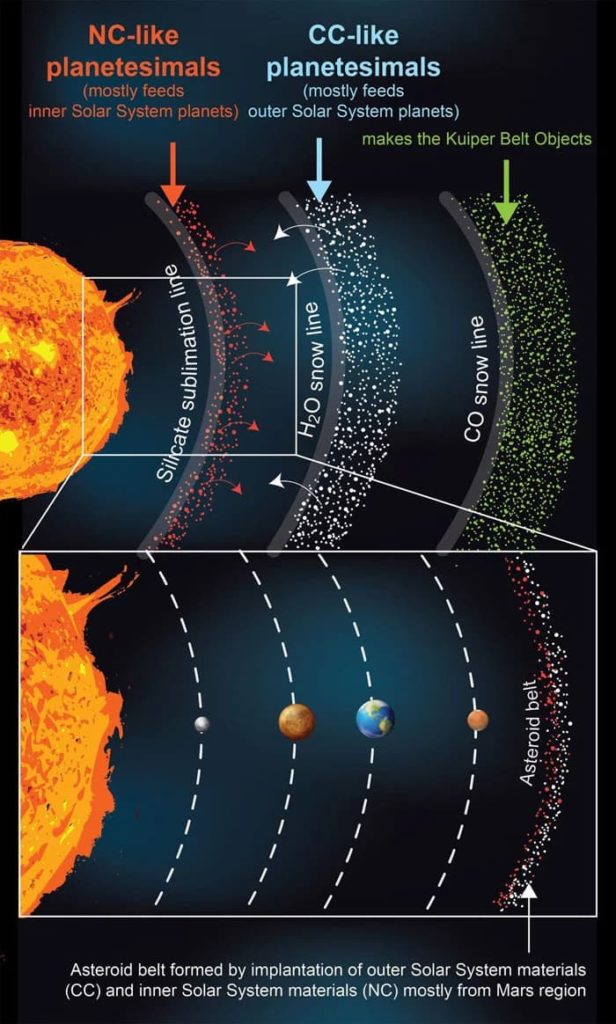
The simulations showed that there may have been three distinct regions where solid particles evaporated into gas, called "sublimation lines". In the line closest to the Sun, or in the hottest region, the solid silicate turns into a gas; In the middle row, the ice may be heated enough to turn into gas; And on the far side, carbon monoxide has turned into a gas.
According to the simulations, solid particles, such as dust, collided with these blocks and began to accumulate.
The effect of the pressure faucet is that it captures dust particles, which is why we see the rings.
Co-author Andrea Isella, professor of physics and astronomy at Rice University, explained.
If these pressure collisions had not existed, the Sun would have quickly devoured the particles, leaving no seeds for the planets to grow.
Our star matured and lost the dust around it, giving rise to planets
With age, the gas and dust surrounding the Sun cooled and sublimation lines moved closer to the Sun. This process allowed dust to accumulate in the sun. planets, or seeds from asteroid-sized planets, which could combine together to form planets.
Our model shows that pressure shocks can concentrate dust, and moving pressure shocks can act like planetary factories.
Increased pressure regulates the amount of material available to form planets in the inner solar system.
Isidoro said in a statement.
According to simulations, the closest ring to the star formed the planets of the inner solar system - Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. The middle ring would eventually become the planets of the outer solar system, while the outer ring formed comets, asteroids, and other small objects in the Kuiper Belt, the region outside of Neptune's orbit.
The researchers found that if they simulated the late formation of the middle ring, it is possible that super-terrestrial planets may have formed in the solar system.

“Friendly zombie fanatic. Analyst. Coffee buff. Professional music specialist. Communicator.”